Liver fat can lead to NASH or NAFLD
The liver helps you digest food, store the energy and remove toxins. Fatty liver infection is a condition wherein fat develops in your liver. There are two principal types:
- Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)
- Alcoholic fatty liver disease, additionally called as alcoholic steatohepatitis.
What is non-alcoholic fatty liver disease?
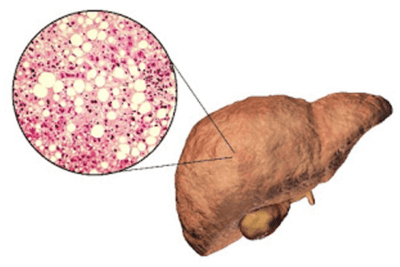 NAFLD is a sort of fatty liver disease that isn’t just related to excessive liquor use. There are two sorts:
NAFLD is a sort of fatty liver disease that isn’t just related to excessive liquor use. There are two sorts:
Simple fatty liver, in which you have fat in your liver yet practically no inflammations or liver cell damage. Simple fatty liver generally doesn’t get awful enough to cause liver harm or inconveniences.
Nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), in which you have inflammation, liver cell damage, and fat in your liver. Irritation and liver cell damage can cause fibrosis, or scarring, of the liver. NASH may eventually cause cirrhosis or liver cancer.
What is alcoholic fatty liver disease?
Alcoholic fatty liver disease is caused due to substantial liquor use. Your liver breaks down most of the liquor you drink so that it can very well be removed from your body. Yet, the process of breaking down of alcohol can create harmful consequences. These substances can harm liver cells, advance aggravation, and debilitate your body’s characteristic natural immunity. The more liquor that you drink, the more you harm your liver. Alcoholic fatty liver disease is the early stage of liquor-related liver disease. The following stages are alcoholic hepatitis and cirrhosis.
NAFLD harms around 25 percent of people around the globe. As the percentage of obesity, type 2 diabetes, and elevated cholesterol are ascending, so is the number of NAFLD. NAFLD is the most common ongoing liver issue.
Alcoholic fatty liver sickness just happens in people who are heavy alcohol consumers, particularly the individuals who have been drinking for an extensive stretch of time. The hazard is higher for substantial consumers who are female, are obese, or have a certain hereditary disease.
Indications of Fatty Liver
 There are a few signs and symptoms of fatty liver, despite the fact that not all of these might be an indication.
There are a few signs and symptoms of fatty liver, despite the fact that not all of these might be an indication.
- Fatigue and weakness
- Slight pain in the abdominal area
- Raised levels of liver enzymes, including AST and ALT
- Raised insulin levels
- Raised triglyceride levels
If fatty liver advances to NASH, the accompanying indications may develop:
- Loss of hunger
- Nausea and vomiting
- Moderate to extreme abdominal pain
- Yellowing of eyes and skin
Actually, at times, you may not even understand you have fatty liver. Therefore, it’s imperative to see your doctor regularly for standard tests and blood tests that can analyse fatty liver at the early, reversible stage.
How Do I Reduce My Liver Fat?

Dietary plans for Getting Rid of Fatty Liver
There are a few things you can do to get yourself free of fatty liver, including getting more fit and decreasing carbs. Additionally, certain food habits can assist you with losing liver fat too.
Getting more fit and avoiding overeating if overweight or obese is perhaps the most ideal approach to get rid of the fatty liver if you are overweight or obese.
Truth be told, weight reduction has shown significant results in advance loss of liver fat in grown-ups with NAFLD, whether or not the weight reduction was achieved by taking up dietary changes alone or along with weight reduction medical procedure and exercise. All these things considered; it led to a huge decline in fatty liver symptoms.
Cut off the Carbs, Especially Refined Carbs
It might appear that the most sensible approach to address fatty liver is decreased dietary fat. In any case, report says that just about 16% of liver fat in individuals with NAFLD originates from dietary fat.
Dietary fat is the fat we include in food (not to be mistaken for body fat, which is the fat stored in our bodies). Dietary Fat is a macronutrient and is an important source of energy in our diet. With around nine calories for every gram, dietary fat constitutes of more than double calories contained in a similar amount of sugar or protein as compared to body fat (every one of which has four calories for every gram). Because of its high in calorie content, having a lot of dietary fat can make it easy for you to outrun your average calorie intake and grow fat.
Most liver fat originates from unsaturated fats in the blood and about 26% of liver fat is shaped in a procedure called de novo lipogenesis (DNL).
Hepatic de novo lipogenesis (DNL) is the biochemical process of breaking down fatty acids from acetyl‐CoA subunits that are produced from many different pathways within the cell, most commonly carbohydrate catabolism.
During DNL, excess carbs are converted into fat. The rate at which DNL happens increases with a high intake of fructose-rich foods and drinks.
Studies have indicated that consuming food less in calories, low in refined carbs may help decrease the effectiveness of NAFLD. These include low-carb food, Mediterranean, and low-glycaemic-index diets.
As per the study, liver fat and insulin resistance decreased significantly when individuals consumed a Mediterranean diet routine than when they consumed a low-fat, high-carb diet, despite the fact that weight reduction was similar during the two eating habits. Although both Mediterranean and exceptionally low-carb diet consumption which has fewer calories have been appeared to reduce liver fat. In a study, 14 obese men with NAFLD followed a Mediterranean ketogenic diet. Following 12 weeks, 13 of the men experienced decreased liver fat, including three who accomplished the total goals of fatty liver.
Exercise can be helpful in reducing Liver Fat symptoms
 Physical activity can be a successful method to diminish liver fat. Studies have shown that taking part in continued exercise or resistance training a few times each week can altogether decrease the amount of fat stored in liver cells, whether or not weight reduction occurs. In a four-week study, 18 obese grown-ups with NAFLD who practiced for 30–60 minutes, five days in every week encountered a 10% reduction in liver fat, despite the fact that their body weight remained same. Similarly, high-intensity interval training (HIIT) has demonstrated to be of great help in diminishing liver fat. In a study of 28 individuals with type 2 diabetes, performing HIIT for 12 weeks showed a noteworthy 39% decrease in liver fat. However, even lower-intensity exercise can be effective in the decline on liver fat. As shown by a large study, it creates the impression that the amount you practice is generally significant. In that review, 22 diabetics who were working out twice every week for a year had comparative decrease in liver fat and stomach fat, whether or not their activity force was viewed as low-to-moderate or moderate to-high. Since working out is considered to be significant in diminishing liver fat, picking something you like doing and can stay with is your best practice.
Physical activity can be a successful method to diminish liver fat. Studies have shown that taking part in continued exercise or resistance training a few times each week can altogether decrease the amount of fat stored in liver cells, whether or not weight reduction occurs. In a four-week study, 18 obese grown-ups with NAFLD who practiced for 30–60 minutes, five days in every week encountered a 10% reduction in liver fat, despite the fact that their body weight remained same. Similarly, high-intensity interval training (HIIT) has demonstrated to be of great help in diminishing liver fat. In a study of 28 individuals with type 2 diabetes, performing HIIT for 12 weeks showed a noteworthy 39% decrease in liver fat. However, even lower-intensity exercise can be effective in the decline on liver fat. As shown by a large study, it creates the impression that the amount you practice is generally significant. In that review, 22 diabetics who were working out twice every week for a year had comparative decrease in liver fat and stomach fat, whether or not their activity force was viewed as low-to-moderate or moderate to-high. Since working out is considered to be significant in diminishing liver fat, picking something you like doing and can stay with is your best practice.
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and its worldwide prevalence matches the development in related diseases like obesity and type II diabetes. Yet, in contrast to obesity and diabetes, basically nobody inclusive of doctors and pharmaceutical organizations talk about it. Simultaneously, as a greater amount of the total population builds up the infection, the quantity of healthy livers available for transplants will probably decrease.
Reference Link : https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PiNRp3WaeVk
